Prerequisites:
Using Serial Port with the Raspberry Pi – Connecting Raspberry Pi’s Serial Port with the onboard STM32 MCU
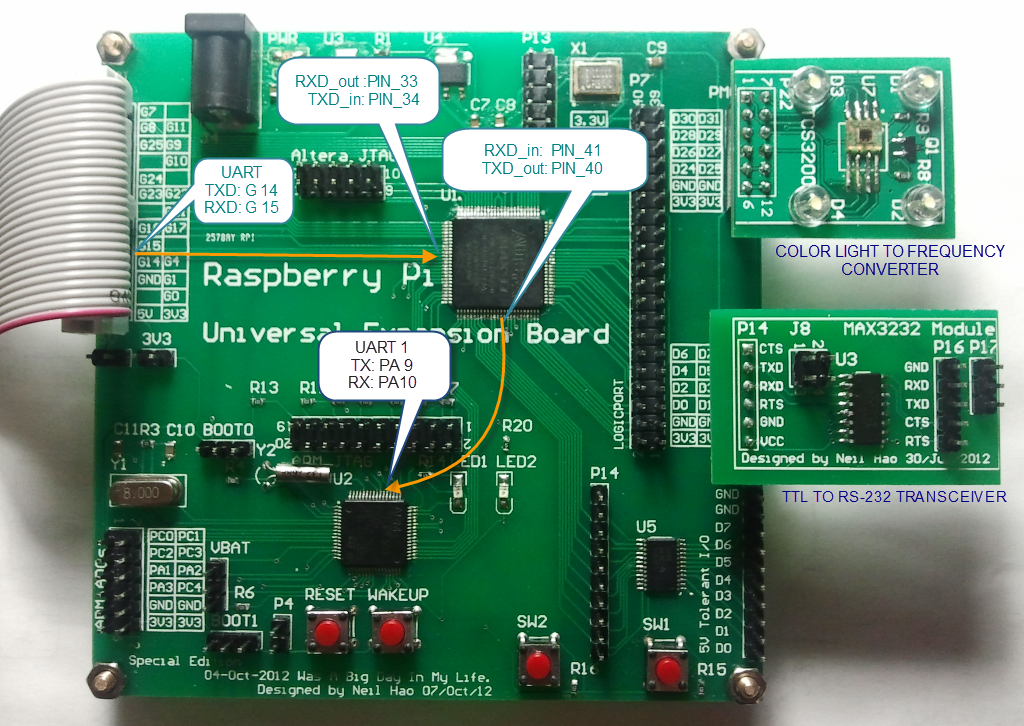
At first, we need to attach the Raspberry Pi to the Universal Expansion Board.
- CPLD Configuration
- Linux Configuration
- Testing
This part is pretty easy since we only need to map the Raspberry Pi’s UART to the onboard STM32 MCU’s UART1 using the CPLD. The following Verilog code can implement the idea:
module RS232(RXD_in,TXD_in,RXD_out,TXD_out); input RXD_in, TXD_in; output RXD_out,TXD_out; assign RXD_out = RXD_in; assign TXD_out = TXD_in; endmodule
Navigate to Quartus -> Assignments -> Pin Planner. The IO need to be configured as following picture.
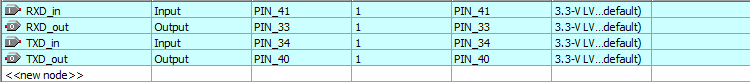
We can flash the design into the CPLD right now.
Edit /boot/cmdline.txt:
sudo vim /boot/cmdline.txt
Originally it contained:
dwc_otg.lpm_enable=0 console=ttyAMA0,115200 kgdboc=ttyAMA0,115200 console=tty1 root=/dev/mmcblk0p2 rootfstype=ext4 elevator=deadline rootwait
Deleted the two parameters involving the serial port (ttyAMA0) to get the following:
dwc_otg.lpm_enable=0 console=tty1 root=/dev/mmcblk0p2 rootfstype=ext4 elevator=deadline rootwait
Edit /etc/inittab:
sudo vi /etc/inittab
We need to comment out following lines in /etc/inittab:
#Spawn a getty on Raspberry Pi serial line T0:23:respawn:/sbin/getty -L ttyAMA0 115200 vt100
Reboot (sudo reboot) to confirm that kernel output is no longer going to the serial. Only one line Uboot message will be printed out during the booting.
![]()
Install the minicom on the Raspberry Pi:
sudo apt-get install minicom
And run it:
minicom -b 9600 -o -D /dev/ttyAMA0
Reset the onboard STM32 MCU, the following information will be printed out:
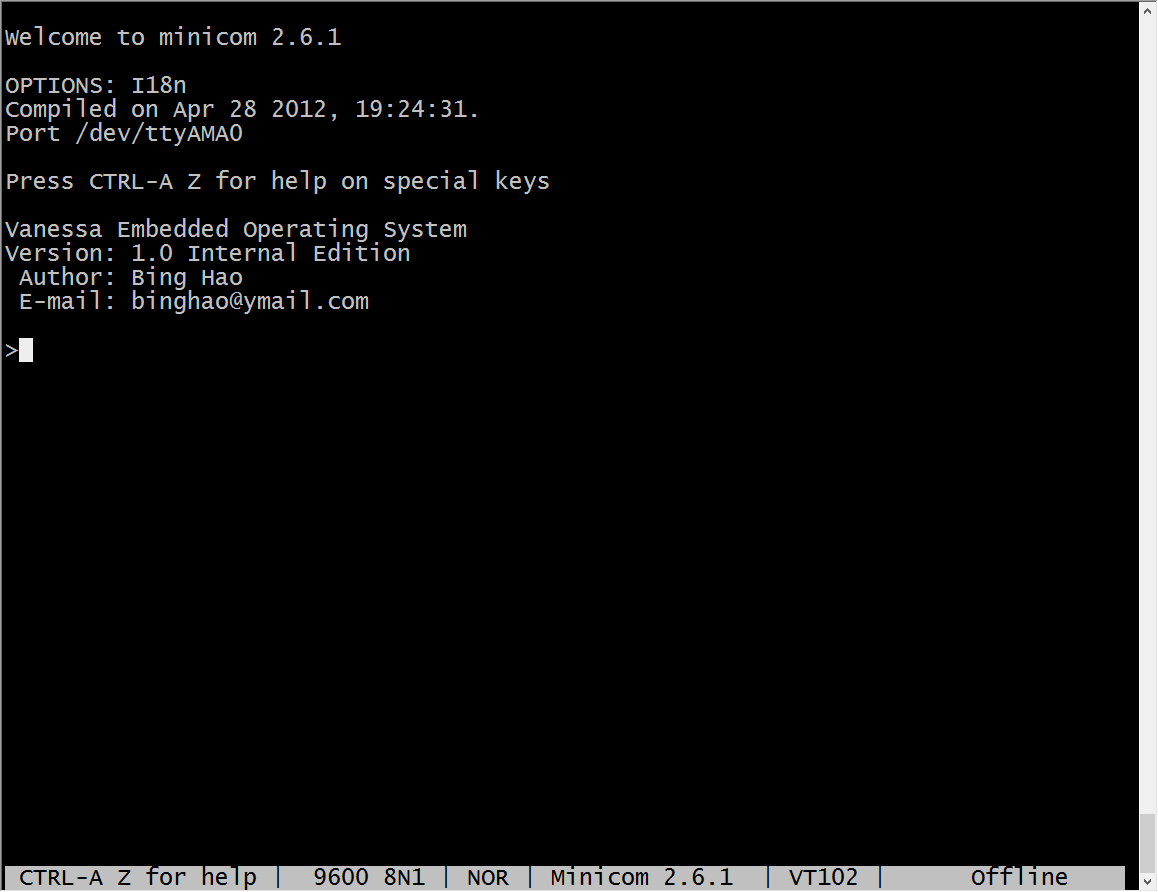
Eventually, the raspberry Pi can talk to the onboard STM32 MCU now.